Understanding Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence, or AI, is actually quite complex to explain. It’s a technology that we usually think of as virtual, something that helps us with our daily tasks or serves as a super assistant that solves all our problems and helps us survive.
Isn’t it strange how AI has become so common that we hardly notice it’s part of our daily lives? Voice assistants are a perfect example. These apps recognize your voice and make calls for you, and they’re right there on our phones.
AI is essential in many fields. For instance, ChatGPT offers significant benefits in research and makes multiple tasks more efficient and automated. Another example is automating tasks, like analog meter displays that have been installed over the past decades. Instead of replacing all these with digital meters, an image detector can now be placed on top of these analog screens. This detector can recognize the needle’s position and convert it into a digital reading, saving data and energy.
AI Aspires to Mimic Human Intelligence but Falls Short
AI aims to emulate human intelligence but is still far from achieving that goal. In essence, AI solves problems differently than traditional code-writing methods. What we want is a machine that makes correct decisions for each assigned task and gains experience over time to solve increasingly complex problems.
The Microcontroller Connection
Understanding edge technology begins with understanding what “edge” means. We’re talking about endpoint devices that include sensors or cameras. These often use microcontrollers instead of more robust technologies since the latter consume a lot of energy and are expensive. Microcontrollers are small CPUs good at basic tasks but with limited memory capacity.
Now, you can find very cheap microcontrollers that can even use cameras like the ESP-32. TinyML comes into play with these less robust processors; it allows you to design efficient programs, much like the early days when computers had limited capacity.
Understanding Neural Networks
Everything starts with the inspiration from neurons. Our brain is amazing. What seems easy for us is often challenging to program traditionally. Scientists were inspired by how one neuron communicates with another.
The connection between two neurons is called a synaptic link. These links can have different connection strengths and transmit information accordingly. A mathematical model based on these principles has been developed, serving as the foundation for AI.
Breaking Down AI Terminology
Artificial Intelligence: This involves machines demonstrating a form of intelligence distinct from natural human and animal intelligence. AI focuses on creating smart devices and systems capable of creatively solving problems that are generally considered human prerogatives.
Machine Learning: A subset of AI that uses techniques enabling computers to recognize data patterns and support AI applications.
Deep Learning: A specialized form of machine learning that uses neural networks to analyze multiple factors in a framework similar to human neural systems.
Why AI is Not Quite Human Yet
Machine Learning involves automatic pattern recognition in data through algorithms. It is particularly useful in complex data settings. For example, a fitness tracker could use Machine Learning algorithms to distinguish between activities like running and swimming based on accelerometer data,
There’s a fundamental difference between how models operate and how humans think and learn. This difference isn’t just about how learning occurs; it’s about the very essence of how problems are understood and solved.
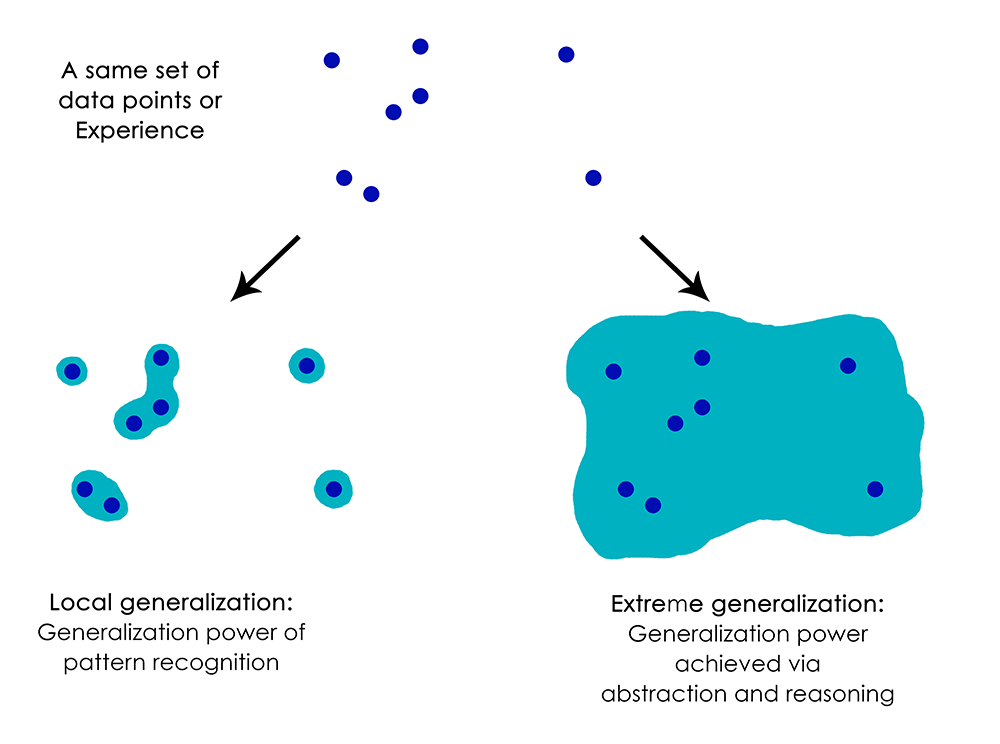
- Local Generalization: Let’s start with deep learning models, which operate on a principle called “Local Generalization.” These models are great at tasks they’ve been trained on but stumble when faced with slightly new challenges. For example, if you train a deep learning model to calculate the right launch conditions for a rocket to land on the moon, it would need thousands or even millions of examples to get it right. The model works well within a narrowly defined set of conditions, but it’s not adaptable. If you change the launch site or any other variable, it has to start from square one.
- Extreme Generalization: Now, consider humans, who are experts at “Extreme Generalization.” Humans can understand situations in a broader, more abstract way. We don’t just react to immediate stimuli; we have a mental model of the world, ourselves, and others. This enables us to adapt to new scenarios rapidly, often without needing any additional information. Imagine you win the lottery: you’ve never experienced that before, but you can immediately plan what to do, thanks to your ability to generalize extremely. You didn’t need a million examples to figure it out, just a solid understanding of money, human behavior, and future planning.
The Contrast
The ability of humans to plan for far-off futures, make abstract connections, and adapt to wholly new scenarios is termed as “Extreme Generalization.” In stark contrast, deep learning models are limited to “Local Generalization,” requiring a large dataset of specific examples to make accurate predictions or decisions.
Introducing Edge Artificial Intelligence or EDGE AI
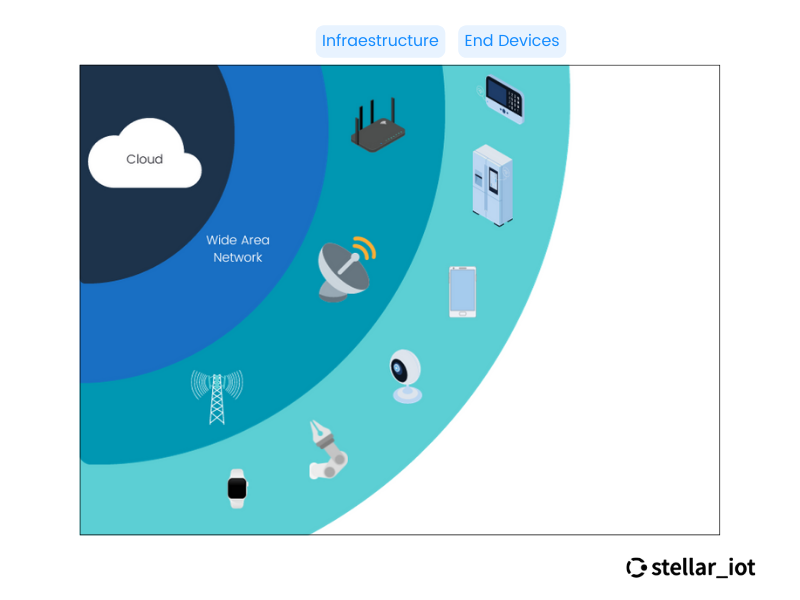 Edge AI combines edge devices, like sensors, with AI technologies. Instead of sending all data to a central server, Edge AI processes it locally on the device, saving costs, reducing latency, and enhancing data privacy.
Edge AI combines edge devices, like sensors, with AI technologies. Instead of sending all data to a central server, Edge AI processes it locally on the device, saving costs, reducing latency, and enhancing data privacy.
Embedded Machine Learning and Tiny Machine Learning
Embedded Machine Learning runs machine learning models on specialized, resource-limited systems. Tiny Machine Learning takes this a step further, applying it to extremely constrained hardware like microcontrollers. These disciplines focus on machine learning inference, which involves making predictions from input data.
The BLERP Factor
A term worth noting is BLERP, an acronym highlighting some standout aspects of Edge AI:
- Bandwidth: More isn’t always better; it consumes more energy and resources. Edge technology saves bandwidth by processing data locally.
- Latency: A significant concern since delays or disruptions in communication services can hamper device functionality.
- Economics: Costs add up quickly, especially when multiple devices are involved.
- Reliability: Internet dependency can be a downside, but Edge AI can increase product reliability by making local decisions.
- Privacy: Edge AI keeps data localized, enhancing privacy and security, which is vital in applications like security camera
Conclusion
Throughout this exploration, we’ve delved into a myriad of aspects that make intelligence, both artificial and human, a topic of unending fascination and complexity. From the underlying algorithms that power machine learning to the brain’s unparalleled capabilities, we’ve seen that the journey towards understanding and replicating intelligence is not linear. One key takeaway is the contrast between Local Generalization and Extreme Generalization, which underscores the gulf that still exists between human cognition and machine learning models.
However, it’s not just about highlighting differences; it’s about recognizing the synergies that can come from integrating machine capability with human-like adaptability and foresight. While AI has made significant strides in numerous domains, the ultimate goal is a harmonious blend of artificial and human intelligence. This equilibrium will allow us to tackle unprecedented challenges, enrich our understanding of the universe, and perhaps even redefine what it means to be intelligent.
As we continue on this fascinating journey, let us be mindful of the nuances that make each form of intelligence unique while remaining open to the endless possibilities that arise when we attempt to merge the best of both worlds.


