 The integration of satellite communication with the Internet of Things (IoT) marks a significant step towards achieving global connectivity. This post explores how satellite IoT is expected to fill the gaps left by terrestrial networks, promising to enhance connectivity in remote and underserved areas across the globe.
The integration of satellite communication with the Internet of Things (IoT) marks a significant step towards achieving global connectivity. This post explores how satellite IoT is expected to fill the gaps left by terrestrial networks, promising to enhance connectivity in remote and underserved areas across the globe.
Satellite IoT: Explained
Once an expensive option reserved for niche applications, satellite communication is transformed. Thanks the evolution in this technology and reductions in costs, it’s now an option of extending IoT connectivity. The development of affordable receiver hardware and the deployment of satellite constellations are making satellite IoT a viable complement to cellular networks.
Satellite Constellations: The Backbone of Satellite IoT
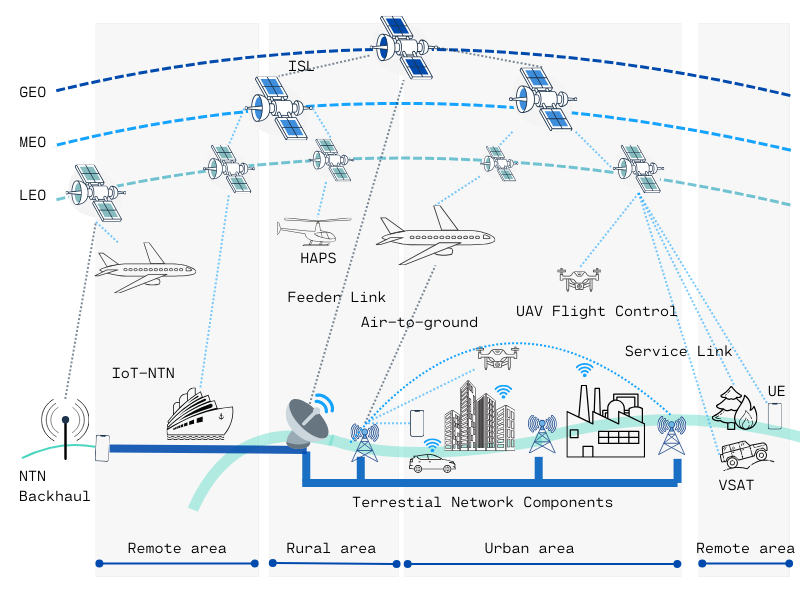
A satellite constellation consists of a group of satellites working together in orbit to provide comprehensive coverage over a large area. Unlike a single satellite that can only cover a part of the Earth at any given time, constellations ensure continuous coverage by having multiple satellites in different orbits. This arrangement allows for a seamless global network, crucial for delivering consistent IoT connectivity across the globe, including in regions where terrestrial networks fall short.
Why Satellite IoT is Key
The value of satellite IoT lies in its ability to provide coverage where terrestrial networks cannot reach. This technology ensures that data from remote sensors, agricultural monitors, or emergency beacons can be transmitted regardless of location. It’s not just about filling coverage gaps; it’s about creating a truly interconnected world where data flows freely from the furthest corners of the earth.
In the coming years, the growth of Non-Terrestrial Network (NTN) IoT services will enable a variety of applications, from emergency services in remote areas to environmental monitoring on a global scale. This expansion is not without challenges, such as integrating these systems with existing networks and ensuring the reliability of the technology through certifications.
Understanding the Technology
The technical foundation of satellite IoT is built on the 3GPP’s NTN architecture, which includes both transparent and regenerative configurations. Transparent systems act as signal repeaters, while regenerative systems process data onboard, allowing for more efficient and flexible communication.
One of the key innovations in satellite IoT is the use of “spot beams” to provide targeted coverage, enhancing efficiency and reducing overlap. However, this technology must overcome challenges like signal delays and frequency shifts, requiring sophisticated solutions to ensure reliable communication.
The introduction of discontinuous coverage, particularly for IoT applications, highlights the adaptability and potential of satellite IoT. By enabling devices to predict when and where they will have connectivity, satellite IoT can support a wide range of applications, from asset tracking to environmental monitoring, even in the most remote areas.
Looking Ahead
As we embrace the potential of satellite IoT, we stand on the brink of a new era of connectivity. This technology doesn’t just promise to bridge the digital divide; it offers a pathway to a future where every device, no matter how remotely located, can be part of the global conversation.
The journey towards this future is complex and filled with challenges, but the potential rewards—unprecedented connectivity, enhanced data collection, and the opening of new frontiers in IoT applications—make it a journey worth undertaking. Satellite IoT is not just an evolution in technology; it’s a fundamental shift in how we connect the world.


