[vc_row][vc_column][vc_single_image image=”224895″ img_size=”Full”][vc_column_text]Originating from NASA’s Apollo program, the concept of the digital twin involved creating identical spacecraft – one sent to space and another kept on Earth for study and simulation. Introduced by Grieves in 2003, a digital twin comprises a physical entity, its digital counterpart, and a connection linking both. This concept has evolved into various subtypes like prototypes, instances, and aggregates.
In today’s business world, we are witnessing a radical transformation, as companies are increasingly adopting the metaverse and advanced simulations. This shift is aimed at driving product development, enhancing experiences, and optimizing operational efficiency. While Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) provide a framework, the concept of Digital Twin (DT) emerges as a pragmatic approach to achieving cyber-physical fusion, bridging the gap between the academic theory of CPS and its practical application in engineering.
The Evolution of the Digital Twin Concept
From 2005-2010, the digital twin concept faced limited reports due to technical constraints. However, the emergence of New Information Technology laid the foundation for its development. NASA and the US Air Force played pivotal roles in defining and applying digital twins in aerospace. By 2014, the three-dimensional structure of digital twins was widely publicized, extending its applications beyond aerospace to automotive, oil and gas, and healthcare industries.
In 2017 and 2018, Gartner identified digital twins as a top technology trend, and Lockheed Martin prioritized them for defense and aerospace. China also embraced digital twins, with researchers exploring the concept of “Digital Twin in the Workshop” and its key technologies. Conferences like the 2017 event at Beihang University stimulated interest and discussion. The 2018 conference at Zhengzhou University of Light Industry sought to delve deeper into digital twin applications, suggesting rapid development in the coming years.
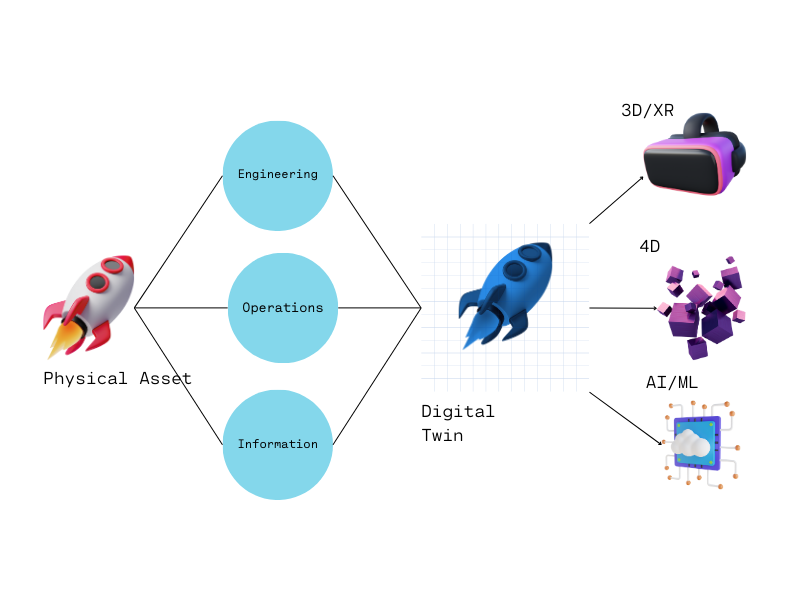
The Essence of Digital Twins
Digital twins are precise virtual replicas in 3D Internet, playing a crucial role in transforming industrial and scientific applications. These connected digital twins enable interaction with the physical world, thanks to AI that autonomously makes decisions based on physical laws. Key attributes of a digital twin include direct observation, physically accurate replication, perfect synchronization, and AI enablement.
Types of digital twins vary:
- Component Twins: Represent the most basic unit, offering a digital visualization of specific components or parts.
- Asset Twins: Replicate two or more components working together, enhancing performance monitoring.
- Process Twins: Digitalize operational processes, production steps, and workflows, offering insights based on analysis.
- System Twins: Provide a comprehensive view of a collection of assets and processes, facilitating design and management of complex asset hierarchies.
Digital twins find applications in numerous industries, improving process efficiency, minimizing downtime, and optimizing outcomes. In manufacturing, they enable real-time monitoring and performance enhancement. In oil and gas, they provide a complete view of process variables for predictive maintenance. In sustainable energy systems, they represent key components for network stability. In healthcare, they create digital representations of patients for informed decision-making. Retailers use them to analyze consumer behavior, and in sustainability, they optimize physical equipment for efficiency.
Building the Right Team for Digital Twin Initiatives
For successful digital twin initiatives, forming diverse teams including technology personnel, engineers, business organizations, data scientists, system integrators, and software development partners is crucial. Identifying talents with experience in modeling resources and processes, critical technology, and data architectures is key.
Common roles in digital twin teams include DevOps/IT engineers, 3D technical artists, software engineers and developers, ML engineers, robotics engineers, mechanical engineers, simulation engineers, industrial designers, UI/UX developers, and planners and managers. Each role has specific responsibilities, from server installation to model development and conceptual design.
The process of building digital twins can start with a smaller team and scale as the use case evolves. Roles require expertise in tools like Docker, Kubernetes, Autodesk Maya, Unity, Unreal, Pytorch, TensorFlow, ROS, Matlab, Ansys Fluent, Adobe Creative Cloud, and Figma. Forming a balanced team with specific skills is essential for successful digital twin development.
Starting with Digital Twins
When starting with digital twins, it’s crucial to avoid overly ambitious plans and focus on a small use case, offering a minimal value solution. This approach allows for gradual scaling and the use of proof-of-concept projects to learn and test quickly, generating momentum and securing resources for future expansions. Measuring and communicating impact, linking results to the original problem and objectives, documenting lessons learned, and best practices ensure success and speed in future digital twin initiatives.
How IoT and Digital Twins Work Together
The proliferation of IoT sensors is key to the viability of digital twins. As IoT devices are refined, digital twin scenarios can include smaller and less complex objects, bringing additional benefits to businesses.
A digital twin is a dynamic virtual replica of a physical asset, process, system, or environment that behaves identically to its real-world counterpart. Built often from conceptual models and IoT data, digital twins enable real-time monitoring of a system’s behavior. Bidirectional communication between digital twins and physical IoT devices allows information exchange and coordinated actions.
Improving Digital Twins with IoT
Real-time data from IoT devices significantly enhance digital twins, providing operators with performance information about the physical object linked to the digital twin in the real world. This information is crucial for efficiently identifying problems and maintaining systems. Network sensors and IoT-connected devices play a vital role in accessing real-time data, allowing digital twins to simulate scenarios and processes more accurately. The combination of simulations with static data and real-time IoT data makes digital twins a powerful tool across various industries, transforming workflows, and improving efficiency.
Ensuring IoT Security: The Crucial Role of Digital Twins
Integrating digital twins with IoT offers significant future benefits, especially regarding security. By connecting digital twin platforms directly to IoT devices, a digital model can be created to ensure the security of devices without physical interaction. As IoT devices integrate more into business environments, the threat of security breaches increases. Digital twins will help address this issue by enabling remote updates, identifying hack origins and breaches, and remotely shutting down IoT devices to prevent potential threats.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][/vc_column][/vc_row]