[vc_row][vc_column][vc_single_image source=”featured_image” img_size=”full” style=”vc_box_rounded” css_animation=”bounceIn”][vc_column_text]People often ask me why I don’t have smart bulbs or other devices automating my home, despite their affordability. To answer this, my response draws on an analogy: I’d rather not invite a Trojan horse into my home.
The term “Trojan horse” means malicious software (malware) hiding in an innocent app or device. Discussing IoT security, we’re highlighting risks tied to IoT devices like smart bulbs, vulnerable to cyberattacks.
Rising Cybersecurity Threats and The Expansion of IoT
Eric Schmidt, former CEO of Google, once noted that every two days, we create as much information as humanity did from the dawn of civilization up until 2003. That equates to roughly five exabytes of data. As the Internet of Things (IoT) grows, and we produce information at this staggering pace, our vulnerabilities intensify. Today, a majority of our devices have “eyes” and “ears”, exposing us more than ever to potential cyber risks.
Surprisingly, in 2021 ransomware was like the biggest threat in cybersecurity. Fast forward to 2023, hackers shift their sights to IoT devices, given their sheer numbers and the vulnerabilities present in many of them. Certainly, manufacturers often shrug off responsibility for these vulnerabilities, leaving IoT lacking terms of security.
The surge in connected devices presents a buffet for cybercriminals, providing a vast “attack surface.” By 2025, we expect nearly 42 billion IoT devices, and vulnerable products within this network will drive the cybercrime cost to an anticipated $10.5 trillion, as Cybersecurity Ventures predicts. [1]
The Hidden Cybersecurity Risks
So, allow me to illustrate how this plays out when you buy one of those $7 smart bulbs that you can control from anywhere. Initially, you might think, “It’s just a bulb; what harm can it do?”. But setting up the bulb connects it to your WiFi network, shared by your computer, your child’s computer, and other devices.
Consider the risks. If a malicious actor accesses the network data of your IoT bulb, they could compromise the private data on all your devices. Imagine the chaos if they use this information to target government sites or other institutions. Even worse, they might access your bank account passwords or personal documents.
That’s why enhancing the security of the Internet of Things (IoT) remains a challenging task. It’s like defending a castle with numerous vulnerable entrances. We need to prioritize security at all stages of an IoT product’s life cycle.
From Risks to Remedies: The Next Chapter in IoT Security
Let’s talk about some actual solutions and interesting developments in the field. Two things worth mentioning are PSA and NIST.
PSA Certified has created a four-stage framework to secure connected devices, with the aim of standardizing security approaches in the IoT. Think of it like a universal safety regulation for car manufacturers. Companies like Espressif, Nordic, and Silicon Lab have embraced this certification for their new cores. [2]
In the United States, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is developing IoT security standards in response to Executive Orders on cybersecurity. [3]
Exploring the Hacker’s Swiss Army Knife: The Flipper Zero
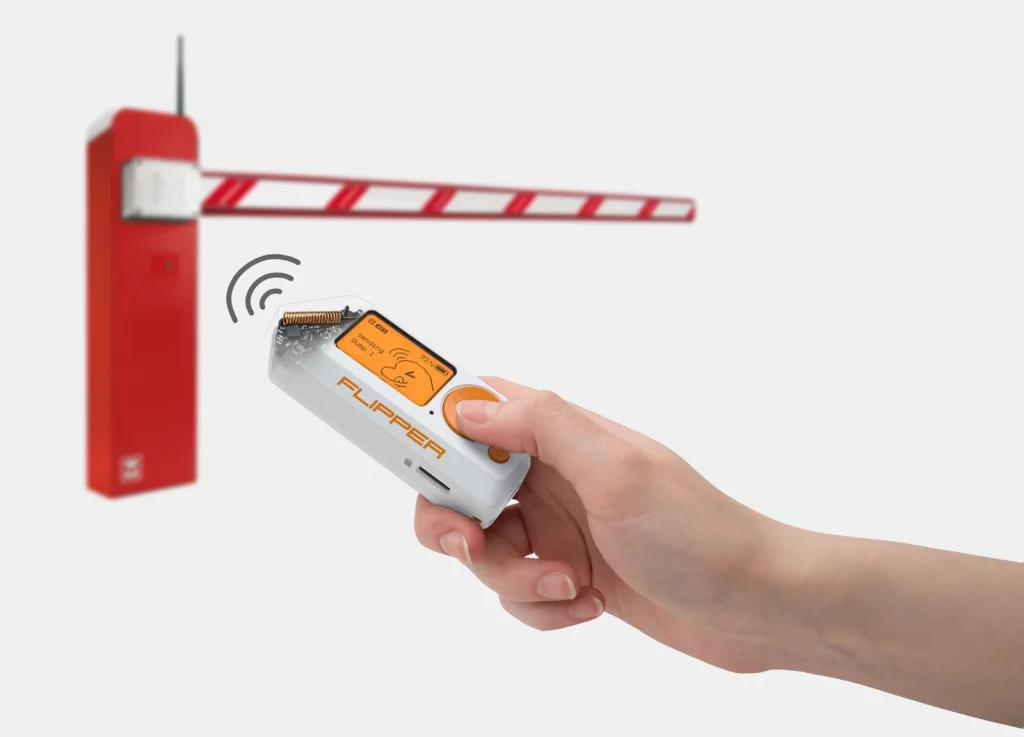

After a brief introduction about security, let’s talk about TikTok’s viral Flipper Zero! a very curious device, as it was inspired by Tamagotchi, but instead of being a virtual pet, it becomes your hacking partner for the Internet of Things (IoT). As you interact with real-world digital systems and perform hacking activities, the Flipper Zero grows and develops its unique personality, making it even more appealing to technology and security enthusiasts. Visit Flipper Zero’s official site. The Flipper Zero is an ideal solution for those interested in IoT hacking without the need to build their own hardware from scratch.
This device, houses a powerful low-power microcontroller and a transceiver. Most importantly, it includes a lithium battery, which means it doesn’t need to be constantly connected to a power source. This provides greater portability and flexibility to carry out tests and explorations in different environments.
So, with this combination of features, the Flipper Zero becomes a complete and autonomous tool for those wishing to understand IoT hacking. Its smart design and versatile capabilities make it an attractive choice for technology and security enthusiasts.
Inside the Flipper Zero: What Makes It Tick?
Speaking of the wireless microcontroller, the STM32WB is based on an Arm® Cortex®-M4 core running at 64 MHz (application processor) and an Arm® Cortex®-M0+ core running at 32 MHz (network processor). It is a self-sufficient solution integrating connectivity features and a general-purpose microcontroller into a single System-on-Chip (SoC). You can check out the open-source repository if you’re interested. Here’s the link.
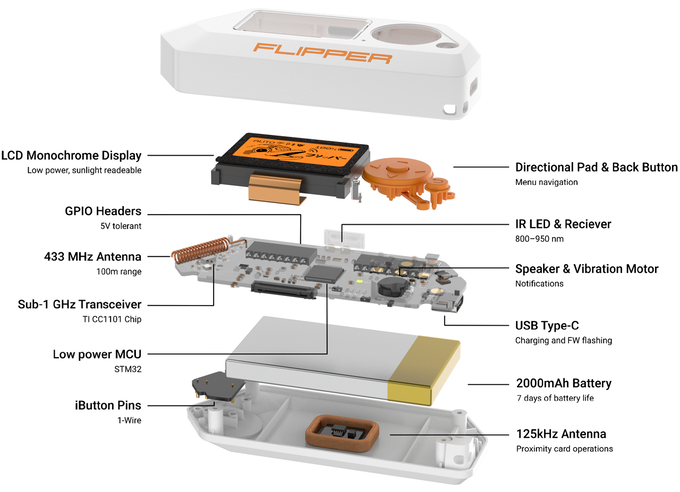
The Flipper Zero offers a wide range of functionalities, ranging from Radio Frequency (RF) hacking to infrared (IR) remote control. With its ability to analyze radio signals, it is a valuable tool for physical security auditing.
In addition, the Flipper Zero allows for the control of IoT devices and can be used for gaming and development projects. It also excels in decrypting and analyzing protocols, with all these capabilities integrated into a single device, the Flipper Zero is ideal for those looking for a multifunctional and autonomous tool for their hacking and pentesting activities.
Embracing a Secure IoT Future
In conclusion, while IoT adds convenience to our lives, it brings a plethora of cyber threats. These risks don’t just impact large infrastructures but seep into our daily lives.
Yet, the silver lining exists. Tools like the Flipper Zero are making IoT security more accessible and engaging. As innovation surges, security must remain at the forefront, converting vulnerabilities into strengths. PSA’s and NIST’s endeavors to standardize IoT security pave the way forward.
Securing the IoT landscape requires a joint effort from manufacturers, cybersecurity professionals, and users.
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]


