[vc_row][vc_column][vc_single_image source=”featured_image” img_size=”full” alignment=”center”][vc_column_text]While browsing the web, I came across an exciting piece of news addressing the evolution of Wi-Fi standards. The Wi-Fi Alliance is leading this shift towards WiFi 7, a new generation that promises exceptional performance and innovative features, in response to the growing demand for faster internet speeds in our homes.
To put it succinctly, WiFi 7 is set to launch in 2024 and is poised to be the natural successor of Wi-Fi 6E
It’s interesting that, personally, I’ve recently experienced the benefits of Wi-Fi 6E, such as its energy efficiency. However, Wi-Fi 7, also known as IEEE 802.11be, is anticipated to bring even more enhancements, including spectrum expansion, increased bandwidth, and a range of new features designed to boost the speed and efficiency of Wi-Fi networks.
A key feature worth mentioning is the so-called “multi-link operation” (MLO), which allows simultaneous transmission between the access point (AP) and a device on different radios, for instance, one using the 5 GHz band and another the 6 GHz band, as long as the devices are compatible. Both bands can be used at the same time to share either redundant or unique data, enhancing reliability with ultra-low and precise latencies, akin to drinking juice with two straws instead of one.
Here’s a small image summarizing the evolution.
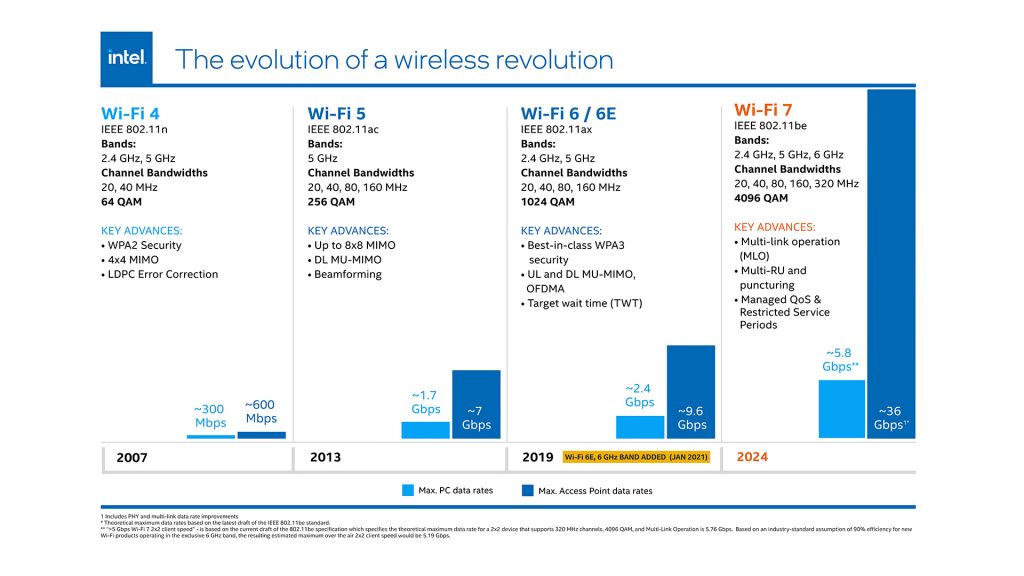
The most notable improvements of Wifi 7 :
Higher speed: Speeds of up to at least 30 Gbps are projected, which is an advancement compared to previous generations like Wi-Fi 6E.
Latency reduction: WiFi 7 aims to minimize latency, a critical aspect for applications requiring quick and consistent responses, such as augmented reality and online gaming.
Support for real-time critical applications: Wi-Fi 7 focuses on real-time data transmission for critical applications, including in industrial and medical realms where reliability and low latency are paramount.
A general advantage of Wi-Fi 7 is its backward compatibility, meaning it can operate with legacy devices on 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and 6 GHz frequencies.
But, what will WiFi 7 bring to the Internet of Things (IoT)?
While specific details haven’t been announced yet, it’s safe to say that WiFi 7 will retain the energy-saving features present in Wi-Fi 6. This boost in energy efficiency reduced latency, and greater connectivity capacity will make it an even more suitable choice for IoT devices, especially those with energy constraints.
Better still, the MLO feature will allow engineers to allocate data performance and real-time control to the critical processes of the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT). In summary, Wi-Fi 7 promises to revolutionize the way we connect and how devices interact in the IoT era.
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]



One Response